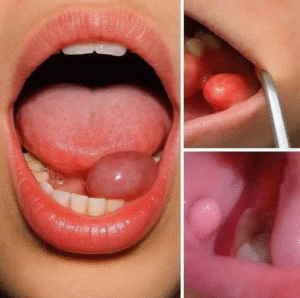
These are the first symptoms of a condition that often goes unnoticed until it progresses, making early recognition critically important. Initially, many people experience subtle changes that are easy to dismiss or attribute to stress, fatigue, or aging. However, these early signs may be the body’s way of signaling something more serious.
Fatigue is often among the first symptoms. Unlike typical tiredness that resolves with rest, this fatigue lingers and may intensify over time, interfering with daily activities. Individuals may find themselves sleeping more but feeling less refreshed.
Changes in appetite or weight can also be early indicators. Some people may lose interest in food, while others might eat more due to emotional changes. Unexplained weight loss or gain should not be ignored, especially when accompanied by other symptoms.
Mood changes are another red flag. People might feel more anxious, irritable, or depressed. They may withdraw from social interactions or lose interest in hobbies and activities they once enjoyed. These changes in behavior can affect personal and professional relationships.
Cognitive symptoms, such as difficulty concentrating, memory lapses, or confusion, often develop subtly. Tasks that were once simple may require more effort. People may struggle to recall names, appointments, or conversations, leading to frustration or embarrassment.
Physical symptoms, though less specific, may include headaches, muscle aches, or digestive issues. Some experience dizziness, numbness, or tingling in their extremities. These can come and go or persist, growing worse with time.
Sleep disturbances are also common in the early stages. People may have trouble falling or staying asleep. Others may sleep excessively, yet still feel unrested. Frequent waking during the night or vivid dreams can also be early warning signs.
Skin changes can occur, including dryness, rashes, or unusual pigmentation. These may appear suddenly and without an obvious cause. Some people notice that cuts or bruises take longer to heal than usual.
Sensory changes, such as blurred vision, ringing in the ears, or altered sense of smell or taste, may occur in the early stages. These changes are often subtle and may not be initially linked to the underlying condition.
Respiratory or cardiovascular symptoms like shortness of breath, irregular heartbeat, or chest discomfort can also develop. These signs might be mild at first but can escalate if left untreated.
Frequent infections or prolonged recovery from minor illnesses can be an early sign of an immune system issue. The body may be struggling to fight off invaders, leaving the person more susceptible to colds, flu, or other infections.
Urinary or bowel habit changes are another early indicator for several conditions. These may include more frequent urination, discomfort during urination, constipation, or diarrhea.
Emotional sensitivity or feeling overwhelmed more easily than usual can suggest underlying neurological or hormonal imbalances. People may cry more often or feel agitated without clear reasons.
Tremors, balance issues, or clumsiness might develop gradually and should not be overlooked. These symptoms could point to neurological conditions, especially if they become more pronounced.
Pain, especially when persistent and unexplained, should always be taken seriously. Chronic back, joint, or abdominal pain may signal deeper issues.
Hair thinning or hair loss in patches can also serve as an early warning sign. This is especially important when it occurs suddenly or is accompanied by changes in skin or nails.
Each of these symptoms on their own may not indicate a serious problem, but a combination of them or a pattern of progression should prompt a visit to a healthcare professional. Early diagnosis can be crucial in managing many conditions effectively, so paying close attention to the body’s signals is key to maintaining long-term health.